Table of Contents
SMC trading strategy is built upon the foundation of modern evolution of price action and institutional price action. Smart money trading strategies attempt to explain how large financial institutions move the market. On price chart, smart money leaves their footprints.
Traders look for the footprints by focusing on key SMC concepts like market structure, structure shifts, liquidity manipulations, and order flow. This article explores the essentials of SMC trading strategy and the concepts used to form the reliable trading strategies.
Understanding the Essentials of SMC Trading Strategy
SMC trading strategies represent a modern and highly refined approach to price action that focuses on understanding why the market moves the way it does. According to SMC founder, these market moves are purely algorithmic. Instead of rely on lagging indicator, SMC traders focus on the logic, behavior, and intention of large institutions.
These institutions include central banks, hedge funds, market makers, liquidity provider, and high-frequency trading firms. Their orders shape the market. It wouldn’t be incorrect to say that they create trend using the algorithm (IPDA).
Smart money cannot enter and exit positions like retail traders. They must accumulate positions over time, manipulate liquidity to fill orders, and engineer market structure shifts. In SMC trading strategy, traders seek to identify these footprints and aligns the trader with institutional behavior.
The core idea of SMC is based on the understanding that markets do not move randomly. They move logically by following liquidity cycles and structural phases.
SMC Trading Strategy Building
It is important to note that building SMC trading strategy is dependent on underlying market structure. The essential concepts are discussed below:
SMC Market Structure
Market structure defines the directional context of the market and provide the framework for interpreting institutional participation. With the help of market structure, you can define your directional trading bias.
Successful trading strategy begins with the establishing directional bias. Identifying directional bias means that understanding whether the market is in a bullish or bearish phase.
In SMC, bias can be determined easily through higher timeframe structure analysis. The bias is bullish when the market forms a sequence of higher highs and higher lows. On the other hand, bearish bias occurs when market continues to print lower lows and lower highs.
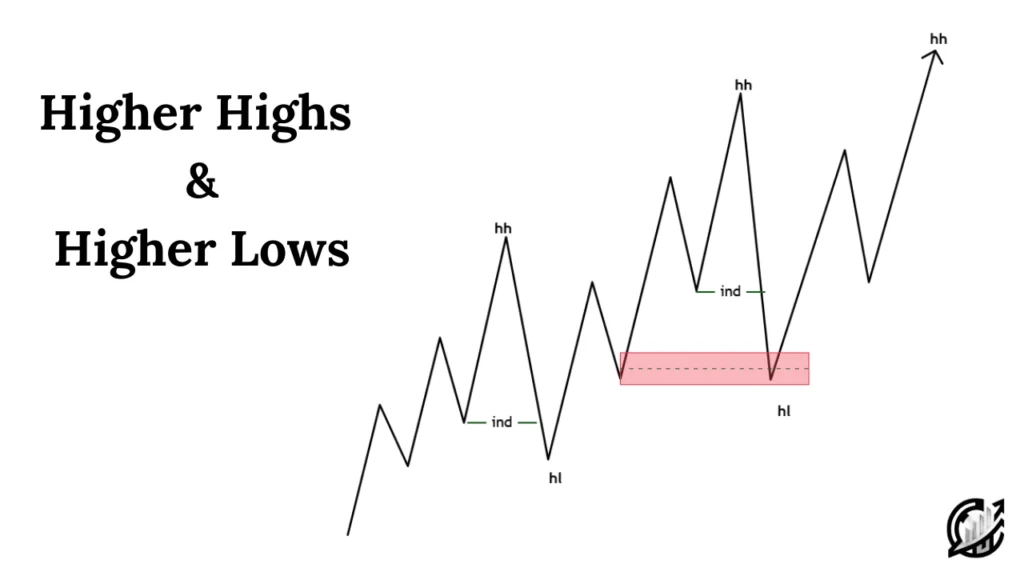
This is the first concept and considered important because institutional traders always operate with directional intent. By aligning your trades with higher timeframe bias, you can ensure that your lower timeframe setups move with institutional momentum.
Liquidity Pools
After establishing the bias, the next step is to locate liquidity pools. Liquidity pools are liquidity zones where a large number of stop-loss orders are resting. Liquidity is the fuel of the market.
There is an idea that smart money cannot execute their massive orders in low-liquidity areas. In order to execute their orders, they hunt liquidity to fill their positions efficiently.
Liquidity zones appear in different forms including equal highs and lows, trendline liquidity, previous session highs and lows, and imbalance or inefficiency zones.
Having an idea of where liquidity lies helps you anticipate where the market might go before it reverse.
Liquidity Sweep
A liquidity sweep is also called liquidity grab or stop-hunt. Liquidity sweep occurs when the market intentionally moves above a key swing high or below the low to trigger stop orders before reversing.
If the market sweeps below a previous low in a bullish market and then forms a strong impulsive move upward, it signals smart money has absorbed sell-side liquidity and is preparing for a bullish phase.
As a trader, you job is to anticipate where liquidity lies, wait for it to be taken, and position your traders after the sweep.
Confirmation through CISD, MSS and CHOCH
After the liquidity sweep, the next step is confirmation of reversal or intent. In SMC trading, you can use three concepts to identify confirmation of reversal or intent. These concepts include CHOCH, CISD, and MSS.
There is a little difference in the three concepts. Change of character occurs on larger timeframe context by breaking higher timeframe major swing low or high depending on the trend.
A CISD is a more dynamic concept that reflect a shift in price momentum or delivery speed. It reflects a shift in price momentum or delivery speed. When the market suddenly transitions from a slow, corrective state to an impulsive displacement, it shows institutional intent to change direction.
Market structure shift is more reliable confirmation signal. It occurs when price breaks the internal structure opposite to the underlying trend after a liquidity grab.
In SMC trading strategy, we can use them together as confirmation signals.
Locating the Trading Zone
After confirming the shift in structure, it is important for you to identify trading zone. As we said, traders should look for the footprints left by smart money
In SMC trading concept, order blocks and FVGs are the two most important zones where institutional orders reside.
Order block is the last bullish or bearish candle before a displacement candle in the opposite direction. On the other hand, FVG is a price imbalance in a strong displacement candle. In the candles, there is an unfilled range between the wicks of consecutive candles.
These zones represent areas of unmitigated institutional orders. There is an idea in SMC trading that when price revisit these areas, it often reacts as pending orders get filled.
Trade Entry Confirmation
This is where precision meets patience. On price chart, identified institutional zone can be false. It is important to note how the price is reacting when approaches your institutional zone. You can wait for lower timeframe confirmation.
Set SL and TP
High-probability SMC trading strategy requires logical stop and target placement. Each trade is based on structure, and so is risk management.
For better risk management, place SL below or above the liquidity sweep or the extreme of the mitigated OB. This ensures your SL lies beyond the area smart money has already used to manipulate liquidity.
Your TP should be the next liquidity pool, FVG or major structural level. If you are entering long after a sweep of equal lows, target the equal highs or imbalance above as your TP zone.
Integrating Time in SMC Trading Strategy
Institutional activity is not random. There are specific sessions where most institutions are active. During these times, the liquidity, volatility, and order flow are at their peak.
There are three core windows of institutional activity: London Open, New York Open, and London Close. Each plays a distinct role in the creation and release of liquidity.
The London Open (3-5 AM EST) marks the first major volatility of the day. The reason is Asian session usually ranges or consolidates. The highs and lows of the Asian session serve as liquidity pools. Market often manipulates the highs and lows forms during the Asian session.
The New York open (8-10 AM EST) amplifies the liquidity even further. There is an idea in SMC trading that liquidity engineered during the London Session is often manipulated again. Many high-probability trades occur when New York hunts London highs or low, and then displaces in the opposite direction.
The New York Close (2-4 PM EST) brings quieter but still meaningful. This is when large positions are hedged, and imbalances are often created. Price frequently returns to mitigate FVGs or OB created earlier in the day.
When SMC is combined with these time-based behaviors, the probability of a setup increases dramatically.
Final Note
SMC trading strategy is not a rigid system or fixed pattern. It is a comprehensive process rooted in understanding why price moves the way it does. The founder of SMC strategy, Micheal, firmly believes that institutions hold the price movements in financial markets. Financial markets carry risk. SMC trading strategy is like other strategies. There is a risk involved in trading financial markets. No single strategy can promise you profits. Research before taking any trading decision.
FAQs
What is SMC Trading Strategy?
SMC trading strategies refers to a institutional trading strategy that contain SMC price action concepts and time confluence. SMC trading strategy explains how institutional traders move the market. It focuses on liquidity, market structure, and order flow rather than indicator.
How does time and session play a role in SMC trading strategy?
Institutional activity peaks during London Open, New York Open, and New York Close. Most liquidity sweeps, displacements, and market structure shifts occur during these windows.
What timeframes are best for SMC trading strategy?
Higher timeframe like daily and 4-hour define directional bias. On the other hand, Lower timeframes such as M5, M1 or M15 are used for refined entries. This combination allows high-probability setups with smaller stop losses.

I’m Aatiq Shah, a dedicated forex and crypto market practitioner with three years of hands-on experience. Currently, I’m working as a Financial Manager. My journey in the world of finance has equipped me with the skills and knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of the forex and crypto markets.