Table of Contents
Institutions and Big money often induce traders to enter, and then they trap them and move market against them. Trapping retail traders is conducted by institutional traders. This idea is rooted in the belief that financial markets are highly influenced by the action and strategies of institutions and “Big Money”. This is because institutions are privileged to see the data which is not accessible to retailers. The concept of “Inducement” is broad in trading markets (forex and other financial markets). SMC and ICT concepts helps in uncover the inducement zone laid by institutions. The article focuses on its meaning and understanding, common inducement scenarios, identification in market structure, and types of inducement.
Understanding Inducement in trading
In general, inducement refers to the notion of persuading someone to do something. The same applies in trading market (forex and other financial markets). Inducement refers to the process by which market movement encourage traders to take positions that are designed to fail. Idea behind inducement is that institutions often manipulate price movements. This attracts wide variety of traders and traps them in wrong trades.
In SMC and ICT trading, understanding the concept practically enhances trading decisions and helps them align with the strategies of institutional players rather than being trapped by them. ICT concepts are helpful in understanding institutional mindset. The tips and tricks of ICT concepts helps us being aware of inducements laid down by institutions.
One thing which beginners have to understand that after careful learning of the ICT trading strategies, we cannot take advantage of every market. Logically, it is not possible to be precise 100 percent. We collect probabilities and select the one which is more logical than the others.
Common Inducement Scenarios
Inducement can be different forms but the purpose behind them remains the same. The ultimate purpose behind the inducement is to trap retail traders. The following scenarios can be considered during market structure analysis:
- One of the common forms of inducement is a false breakout. Normally price breaches specific levels (especially support or resistance), encourages traders to enter trades in the direction of the breakout. After enough liquidity collection, the price reverse and stops them out.
- Inducement often targets liquidity pools, areas where a significant number of stop-loss orders or pending orders are likely to be triggered. For example, just above a resistance level or below a support level, smart money may drive the price to these levels to “grab” the liquidity before reversing the price.
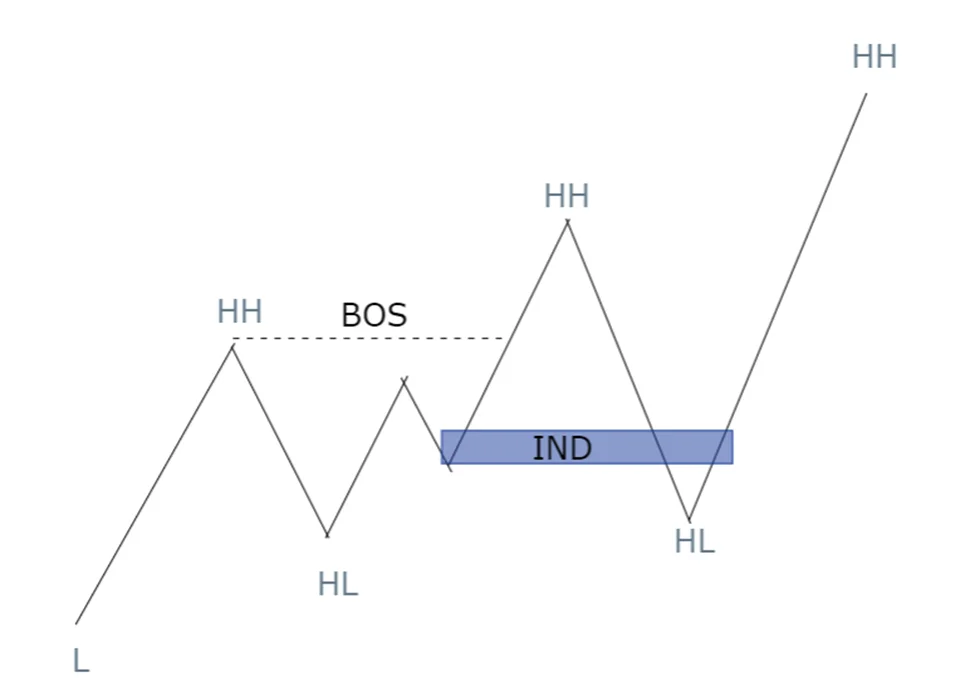
- Third scenario is the most important for traders to understand. An Order Block can be an inducement. Now it confuses traders but an order block can also be an inducement. After break of structure, order block in first pullback often considered as inducement zone because often traders consider the zone as Order block and execute trade from there.
These are few scenarios that should be considered in market structure analysis. Our concern in this article is the third scenario often neglected by traders.
Identification of Inducement in Trading
Understanding inducement is a critical concept especially if the inducement is the order block of first pullback after break of structure or change of character. To effectively identify and understand inducement, it’s crucial to have a solid grasp of key market structure concepts like “Valid Pullback,” “Break of Structure (BOS),” and “Change of Character (CHOCH).” These elements play a central role in distinguishing between genuine market movements and inducements designed to trap retail traders.
- A valid pullback is a retracement within a trend. It is a corrective phase of the trend where the market moves against the trend before resuming its trending direction.
- A break of structure occurs when price continues its trending movement rather than reversing the trend. However, not all breaks are genuine. This is where understanding inducement becomes crucial.
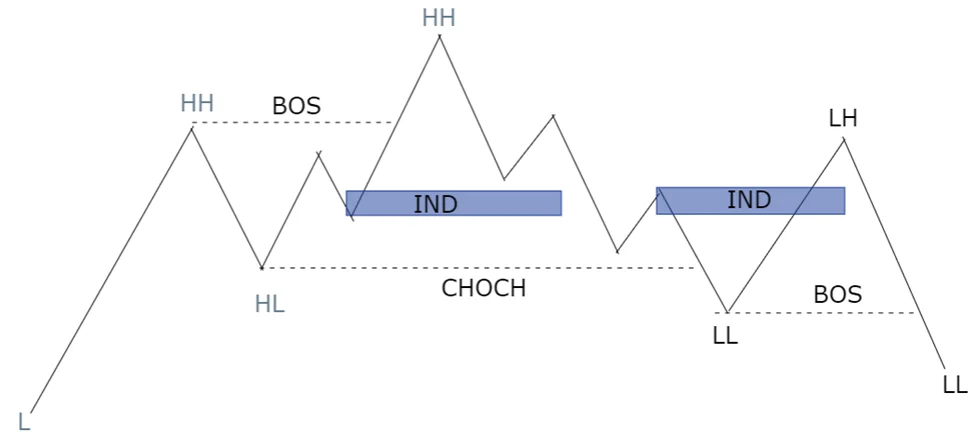
- Change of character refers to a shift in a market structure. Instead of continuing of the trend, market reverse its trending movement. Identification of inducement within the context helps traders avoid false signals.
These three are crucial concepts in understating market structure and identification of inducement within the range.
Types of Inducement based on Structure Breaks
Inducement can be analyzed and identified in two primary scenarios. First scenario is following a Break of Structure, and the second one is Change of Character.
After a BOS, the market often sees a pullback before continuing in the direction of the break. Retail traders might interpret the Order Block in pullback as an opportunity to enter the market in the direction of the break. However, if this pullback is part of an inducement strategy, smart money might push the price to these levels to trap retail traders before continuing the trend. Identifying inducement here involves recognizing whether the pullback is a valid one or merely a setup to trigger retail entries.
In the case of CHOCH, inducement often occurs with the very first pullback after the market changes its character. This is because the initial retracement following a CHOCH can be a trap designed to lure retail traders into thinking the old trend will continue, while in reality, the market is preparing to move in the opposite direction. To identify inducement here, traders should look back at the price leg leading to the CHOCH and find a valid pullback. This pullback can serve as an inducement zone where retail traders are trapped before the new trend solidifies.
Identification of Inducement in market analysis can be used in our favor. We simply wait for the price to grab the inducement level. After successful grabbing of the liquidity, we will place our entries accordingly. By understanding and identifying key concepts, a traders can better recognize when they are being induced and avoid falling into these traps.
Final Note
Understanding inducement and its connection to market structure is crucial for aligning with institutional traders and avoiding common traps. Always analyze “Valid Pullbacks,” “BOS,” and “CHOCH” to identify potential inducement zones. Trading forex involves significant risk, and past performance is not indicative of future results. Ensure you fully understand the risks and use appropriate risk management strategies before engaging in live trading.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is inducement (IND) in trading?
Inducement refers to the practice by institutional traders of manipulating price action to lure retail traders into taking positions that are likely to fail, often by triggering stop-loss orders or false breakouts.
Can inducement occur in any market, or is it specific to forex?
Inducement can occur in any financial market, including forex, stocks, commodities, and cryptocurrencies. The principles of market structure and smart money manipulation apply across various asset classes.
Is inducement always intentional by institutional traders?
While not always intentional, inducement is often a byproduct of the need for liquidity by institutional traders. Their large orders can influence price action in ways that trap retail traders, whether by design or as a consequence of their trading activities.
How to identify an inducement in the forex market?
To identify inducement, you need to analyze “Valid Pullbacks,” “Break of Structure (BOS),” and “Change of Character (CHOCH).” Inducement often occurs around these structural elements where retail traders are likely to be trapped.

I’m Aatiq Shah, a dedicated forex and crypto market practitioner with three years of hands-on experience. Currently, I’m working as a Financial Manager. My journey in the world of finance has equipped me with the skills and knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of the forex and crypto markets.